YAML 概述
YAML 是 “YAML Ain’t a Markup Language” (YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。
在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:”Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言), 这种语言以数据为中心,而不是以标记语言为重点
以前的配置文件,大多数都是使用 xml 来配置;比如一个简单的端口配置,使用 yaml 标记数据更轻便
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8# 传统 xml 配置:
<server>
<port>8081<port>
</server>
# yaml 配置:
server:
port: 8081
yaml 基础语法
- YAML 语法要求严格!
- 空格不能省略,缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
- 以缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左边对齐的一列数据都是同一个层级的。
- 属性和值的大小写十分敏感的。
- 缩进时不允许使用 Tab 键,只允许使用空格
字面量
- 字面量(数字,布尔值,字符串)直接写就可以 , 字符串默认不用加上双引号或者单引号
- 注意:
双引号,不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符 , 特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思;
- 比如 :
name: "张 \n 三",结果会输出二行
- 比如 :
单引号,会转义特殊字符 , 特殊字符最终会变成和普通字符一样输出
- 比如 :
name: "张 \n 三’输出 :张 \n 三
- 比如 :
对象、Map
在下一行来写对象的属性和值得关系,注意缩进;比如:
1
2
3student:
name: zs
age: 3行内写法
1
student: {name: zs,age: 3}
数组
用
-值表示数组中的一个元素,比如:1
2
3
4pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig行内写法
1
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
properties 配置文件写法
1
2com.code.services[0]=service1
com.code.services[1]=service2
YAML 编写规范
编码规范
- 文档使用 Unicode 编码作为字符标准编码,例如 UTF-8
注释
使用
#来表示注释内容功能注释标在开头
语句注释标在行后
1
2
3
4
5
6
7# 客户订单
date: 2015-02-01
customer:
name: Jai
items:
no: 1234 # 订单号
descript: cpu
缩进
- 使用空格 (2 个空格)作为嵌套缩进工具。通常建议使用两个空格缩进,不建议使用 tab (甚至不支持)
序列
使用
-(横线+ 单个空格) 表示单个列表项1
2
3--- # 文档开始
- 第一章 简介
- 第二章 设计目录使用
[]表示一组数据1
2--- # 文档开始
[blue, red, green]组合表示。每个结构都可以嵌套组成复杂的表示结构。
1
2
3
4--- # 文档开始
- [blue, red, green] # 列表项本身也是一个列表
- [Age, Bag]
- site: {osc:www.oschina.net, baidu: www.baidu.com} # 这里是同 键值表 组合表示
键值表
使用
:(冒号 + 空格)表示单个键值对1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8# 客户订单
date: 2015-02-01
customer:
- name: Jai
items:
- no: 1234 # 订单号
- descript: cpu
- price: ¥800.00使用
{}表示一个键值表1
2
3
4
5# 客户订单
date: 2015-02-01
customer:
- name: Jai
items: {no: 1234, descript: cpu, price: ¥800.00}?(问号+空格)表示复杂的键。当键是一个列表或键值表时,就需要使用本符号来标记。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8# 使用一个列表作为键
? [blue, reg, green]: Color
# 等价于
? - blue
- reg
- gree
: Color组合表示。每个结构都可以嵌套组成复杂的表示结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22Color:
- blue
- red
- green
# 相当于 (也是 JSON 的表示)
{Color: [blue, red, green]}
div:
- border: {color: red, width: 2px}
- background: {color: green}
- padding: [0, 10px, 0, 10px]
# 使用缩进表示的键值表与列表项
items:
- item: cpu
model: i3
price: ¥800.00
- item: HD
model: WD
price: ¥450.00
# 上面使用 “-” 前导与缩进来表示多个列表项,相当于下面的 JSON 表示
items: [{item:cpu, model:i3, price:¥800.00}, {item:HD, model:WD, price: ¥450.00}]
长文本块
name: |: 会保留回车换行
保留块中已有的回车换行。相当于段落块
1
2yaml: | # 注意 ":" 与 "|" 之间的空格
JSON 的语法其实是 YAML 的子集,大部分的 JSON 文件都可以被 YAML 的解释器解释。
yaml: >回车变空格
使用 “>” 和文本内容缩进表示的块:将块中回车替换为空格,最终连接成一行。
1
2
3yaml: > # 注意 ":" 与 ">" 之间的空格,另外可以使用空行来分段落
JSON 的语法其实是 YAML 的子集,
大部分的 JSON 文件都可以被 YAML 的解释器解释。
多行变一行
使用定界符
“”(双引号)、‘’(单引号)或回车表示的块:最终表示成一行。1
2
3
4
5
6yaml: # 使用回车的多行,最终连接成一行。
JSON 的语法其实是 YAML 的子集,
大部分的 JSON 文件都可以被 YAML 的解释器解释。
yaml: # 使用了双引号,双引号的好处是可以转义,即在里面可以使用特殊符号
"JSON 的语法其实是 YAML 的子集,
大部分的 JSON 文件都可以被 YAML 的解释器解释。"
数据类型
常用基本类型
对一些常用数据类型的表示格式进行了约定,包括:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14integer: 12345 # 整数标准形式
octal: 0o34 # 八进制表示,第二个是字母 o
hex: 0xFF # 十六进制表示
float: 1.23e+3 # 浮点数
fixed: 13.67 # 固定小数
minmin: -.inf # 表示负无穷
notNumber: .NaN # 无效数字
null: # 空值
boolean: [true, false] # 布尔值
string: '12345' # 字符串
date: 2015-08-23 # 日期
datetime: 2015-08-23T02:02:00.1z # 日期时间
iso8601: 2015-08-23t21:59:43.10-05:00 # iso8601 日期格式
spaced: 2015-08-23 21:59:43.10 -5 # ?
自定义数据类型
!(叹号)显式指示类型,或自定义类型标识。单叹号通常是自定义类型,双叹号是内置类型1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42isString: !!str 2015-08-23 # 强调是字符串不是日期数据
picture: !!binary | # Base64 图片
R0lGODlhDAAMAIQAAP//9/X
17unp5WZmZgAAAOfn515eXv
Pz7Y6OjuDg4J+fn5OTk6enp
56enmleECcgggoBADs=
#下面是内置类型
!!int # 整数类型
!!float # 浮点类型
!!bool # 布尔类型
!!str # 字符串类型
!!binary # 也是字符串类型
!!timestamp # 日期时间类型
!!null # 空值
!!set # 集合
!!omap, !!pairs # 键值列表或对象列表
!!seq # 序列,也是列表
!!map # 键值表
#下面是一些例子:
--- !!omap
- Mark: 65
- Sammy: 63
- Key: 58
--- !!set # 注意,“?”表示键为列表,在这里列表为 null
? Mark
? Sammy
? Key
# 下面是自定义的类型或标识
%TAG ! tag:clarkevans.com,2002: # % 是指令符号
--- !shape
# Use the ! handle for presenting
# tag:clarkevans.com,2002:circle
- !circle
center: &ORIGIN {x: 73, y: 129}
radius: 7
- !line
start:
finish: { x: 89, y: 102 }
- !label
start:
color: 0xFFEEBB
text: Pretty vector drawing.
锚点与引用
第一步:使用
&定义数据锚点(即要复制的数据)第二步:使用
*引用上述锚点数据(即数据的复制目的地)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
hr:
- Mark McGwire
# Following node labeled SS
- &SS Sammy Sosa # 定义要复制的数据
rbi:
- *SS # Subsequent occurrence 这里是数据复制目标
- Ken Griffey
配置文件
配置文件 的作用用于修改 SpringBoot 自动配置的默认值 (SpringBoot 在底层已经配置好的属性)。
SpringBoot 使用一个全局的配置文件 , 配置文件名称是固定的。
application.propertiesapplication.yml
注意:如果 yml 和 properties 同时都配置,并且没有激活其他环境 , 默认会使用 properties 配置文件
在代码里指定配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class SpringbootrestdemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootrestdemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
随机数
- 配置文件还可以编写占位符生成随机数
${random.value}${random.int}${random.long}${random.int(10)}${random.int[1024,65536]}
引用配置的值
如果没有可以指定默认值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13person:
name: fulsun${random.uuid}
age: ${random.int}
happy: false
birth: 2020/02/02
lists:
- eat
- sleep
- code
dog:
name: ${person.hello: 旺旺}_dog # 没有 person.hello 就使用旺旺
age: 2
map: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
Bean 读取 yaml 文件
@Value 注入属性值
编写配置文件
1
2dog:
name: 旺旺财使用
@Value给 bean 注入属性值1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11package top.fulsun.helloworld.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//注册 bean 到容器中
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
//有参无参构造、get、set 方法、toString() 方法
}在 SpringBoot 的测试类下注入狗狗输出一下;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
class HelloworldApplicationTests {
// 多个 Dog 示例时候 @Qualifier("name") 注解来指明注入的实例
//将狗狗自动注入进来
private Dog dog;
void contextLoads() {
//打印输出
System.out.println(dog);
}
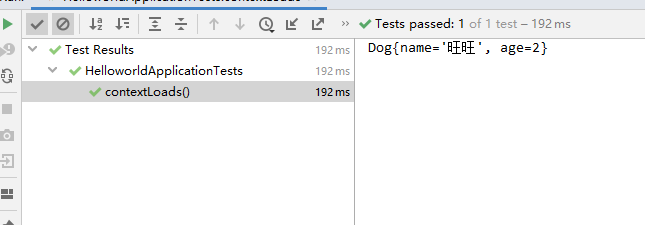
}结果成功输出,@Value 注入成功,这是我们原来的办法。
添加注解处理器
如果希望 IDEA 会提示类中自定义的属性,需要配置注解处理器,具体查看文档
导入配置文件处理器
1
2
3
4
5
6<!-- 导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示,需要重启 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
bean 读取 yaml 的值
yaml 配置文件强大的地方在于,他可以给我们的实体类直接注入匹配值,类的字段必须有公共 setter 方法。
在 springboot 项目中的 resources 目录下新建一个文件 application.yml,编写一个实体类 Dog;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//注册 bean 到容器中
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
//有参无参构造、get、set 方法、toString() 方法
}编写一个复杂一点的实体类:Person 类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11//注册 bean 到容器中
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean isHappy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> map;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
//有参无参构造、get、set 方法、toString() 方法
}我们来使用 yaml 配置的方式进行注入,编写一个 yaml 配置文件
application.yml!1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13person:
name: fulsun
age: 3
happy: false
birth: 2020/02/02
lists:
- eat
- sleep
- code
dog:
name: 旺旺
age: 2
map: {k1: v1,k2: v2}我们刚才已经把 person 这个对象的所有值都写好了,我们现在来注入到我们的类中!
@ConfigurationProperties作用:将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中;prefix = “person”: 将配置文件中的 person 下面的所有属性一一对应- 配置文件的 key 值 和 属性的值设置为不一样,则结果会输出为 null,注入失败
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11//注册 bean
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean isHappy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> map;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
}确认以上配置都 OK 之后,新建测试类测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class HelloworldApplicationTests {
Person person; //将 person 自动注入进来
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person); //打印 person 信息
}
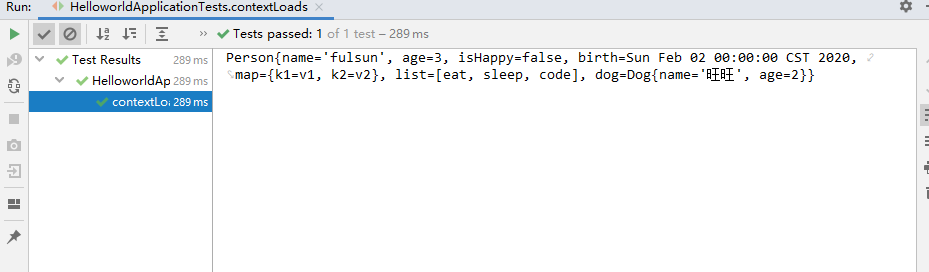
}结果:属性值注入成功!
Configuration Processor
Spring Boot Configuration Processor 依赖添加后,我们在 application.properties 和 application.yml 中写配置的时候会有自动提醒
原理:重新 build 项目之后,configuration processor 会为我们在 target/classes/META-INF 下创建一个 spring-configuration-metadata.json 文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27{
"groups": [
{
"name": "com.code",
"type": "top.fulsun.test.FooProperties",
"sourceType": "top.fulsun.test.FooProperties"
}
],
"properties": [
{
"name": "com.code.age",
"type": "java.lang.Integer",
"sourceType": "top.fulsun.test.FooProperties"
},
{
"name": "com.code.foo",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"sourceType": "top.fulsun.test.FooProperties"
},
{
"name": "com.code.name",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"sourceType": "top.fulsun.test.FooProperties"
}
],
"hints": []
}configuration processor 允许我们标记某一个属性为 deprecated, 我们可以通过添加
@DeprecatedConfigurationProperty注解到字段的 getter 方法上,来标示该字段为 deprecated,重新 build 项目后,当我们再编写配置文件时,已经给出了明确 deprecated 提示:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10{
"name": "com.code.name",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"sourceType": "top.fulsun.test.FooProperties",
"deprecated": true,
"deprecation": {
"reason": "change name ",
"replacement": "none"
}
}
@ConfigurationProperties
@ConfigurationProperties注解要想生效,需要加载到 Spring 用程序上下文中我们可以通过下面几种方式将其添加到应用上下文中
可以通过添加
@Component注解让 Component Scan 扫描到,只有当类所在的包被 Spring@ComponentScan注解扫描到才会生效,默认情况下,该注解会扫描在主应用类下的所有包结构我们也可以通过 Spring 的 Java Configuration 特性实现同样的效果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class PropertiesConfig {
public Person Person(){
return new Person();
}
}可以使用
@EnableConfigurationProperties(class)+@ConfigurationProperties(prefix)注解让我们的类被 Spring Boot 所知道,在该注解中其实是用了@Import(EnableConfigurationPropertiesImportSelector.class)实现1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class DemoApplication {
// 需要从容器中获取并注入此类
private Person person;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
@ConfigurationProperties 类的最佳方式是什么?
模块化的应用程序,我们只需要提供自己的
@ConfigurationProperties类,在特定于模块的 @Configuration 类上使用@EnableConfigurationProperties(class)的方式引入即可。不建议在应用启动类上使用@EnableConfigurationProperties1
2
3
4
public class UserConfig {
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean isHappy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> map;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
}
忽略属性错误
属性配置错误的值时,如定义 boolean,注入时配置文件填写为 string 类型,不希望 Spring Boot 应用启动失败,我们可以设置
ignoreInvalidFields属性为 true (默认为 false)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
// 出现问题 Spring Boot 将会设置 enabled 字段为我们在 Java 代码里设定好的默认值。
// 如果我们没有设置默认值,enabled 将为 null,
private Boolean enable = Boolean.TRUE;
}
多余属性检验
application.properties 文件提供了多余的属性
- 默认情况下,Spring Boot 会忽略那些不能绑定到
@ConfigurationProperties类字段的属性
- 默认情况下,Spring Boot 会忽略那些不能绑定到
然而,当配置文件中有一个属性实际上没有绑定到
@ConfigurationProperties类时,我们可能希望启动失败。为了实现上述情况,我们仅需要将
ignoreUnknownFields属性设置为 false (默认是 true)1
ignoreUnknownFields未来 Spring Boot 的版本中会被标记为 deprecated. 因为我们可能有两个带有@ConfigurationProperties的类,同时绑定到了同一个命名空间 (namespace) 上,其中一个类可能知道某个属性,另一个类却不知道某个属性,这样就会导致启动失败。
Bean 读取 properties 文件
我们上面采用的 yaml 方法都是最简单的方式,开发中最常用的;也是 springboot 所推荐的!
配置文件除了 yml 还有我们之前常用的 properties
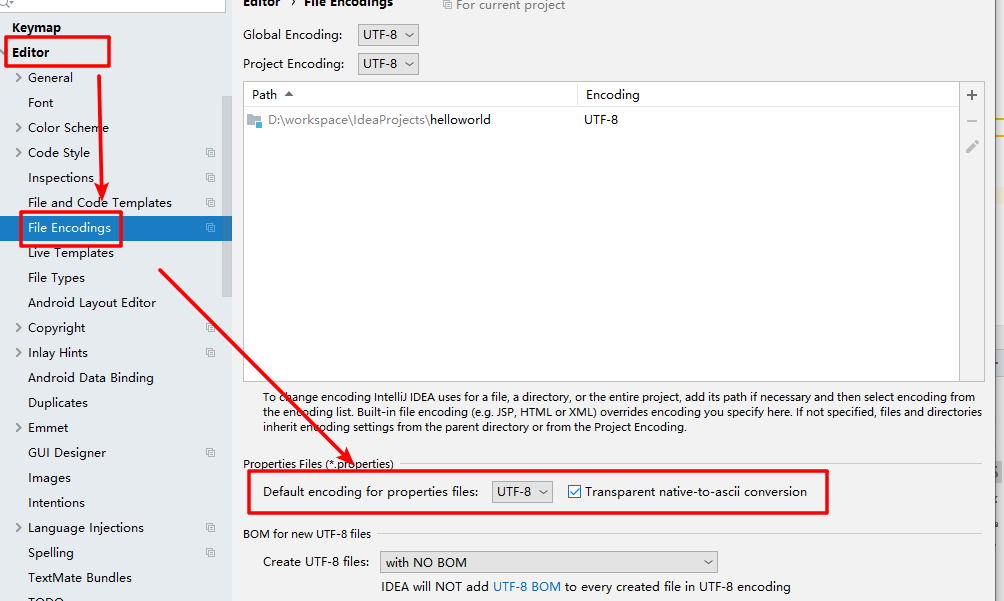
注意:properties 配置文件在写中文的时候,会有乱码 , 我们需要去 IDEA 中 settings–>FileEncodings 中配置编码格式为 UTF-8
新建一个实体类 User
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8//注册 bean
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
//......
}编辑配置文件 user.properties
1
2
3user1.name=zhangsan
user1.age=18
user1.sex=男
@Value 注入属性值
我们在 User 类上使用@Value 来进行注入!
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件;@configurationProperties:默认从全局配置文件 application.properties 中获取值;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11//注册 bean
public class User {
//直接使用@value
//从配置文件中取值
private String name;
// #{SPEL} Spring 表达式
private int age;
// 字面量
private String sex;
}
Springboot 测试
测试类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
class DemoApplicationTests {
User user;
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(user);
}
}结果正常输出:
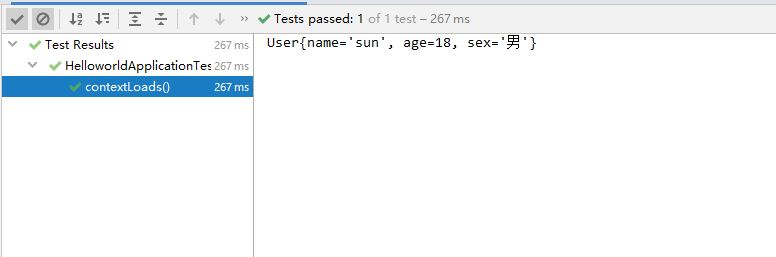
@PropertySource
Spring 框架提供了 PropertySource 注解,目的是加载指定的属性文件,可以加载 properties 配置文件的,不能加载 YAML 配置文件;
value:加载 classpath 路径下的 test.properties 配置文件;
ignoreResourceNotFound:当指定的配置文件不存在是否报错,默认是 false ; 比如上文中指定的加载属性文件是 test.properties。如果该文件不存在,则 ignoreResourceNotFound 为 true 的时候,程序不会报错,如果 ignoreResourceNotFound 为 false 的时候,程序直接报错。实际项目开发中,最好设置 ignoreResourceNotFound 为 false。该参数默认值为 false;
encoding:用于指定读取属性文件所使用的编码,我们通常使用的是 UTF-8;
name:这个值在 Springboot 的环境中必须是唯一的,如果不设置,则值为:“class path resource [test.properties]”;此值也可以不用设置;若想深入研究,可查资料继续研究;
注入方式对比
| @ConfigurationProperties | @Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 功能 | 批量注入配置文件中的属性 | 一个个指定 |
| 松散绑定(松散语法) | 支持 | 不支持 |
| SpEL | 不支持 | 支持 |
| JSR303 数据校验 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 复杂类型封装 | 支持 | 不支持 |
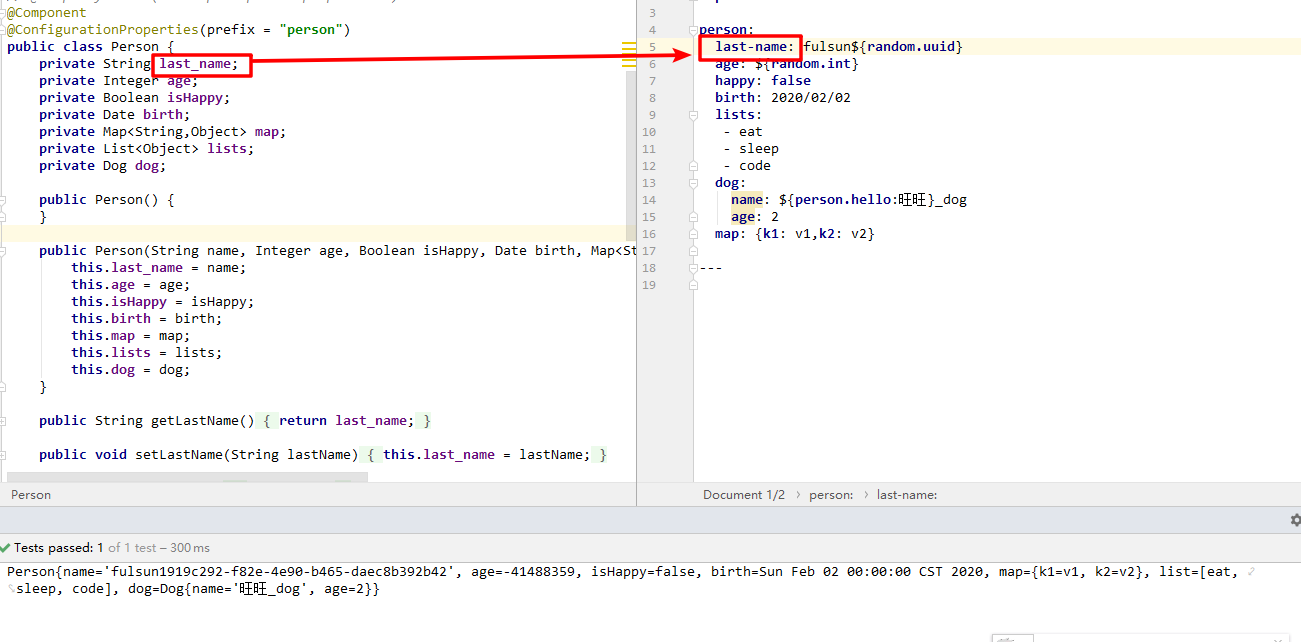
@ConfigurationProperties只需要写一次即可 ,@Value则需要每个字段都添加松散绑定:比如我的 yml 中写的 last-name(- 后面跟着的字母默认是大写),Bean 中有 lastName 也可以注入成功。
JSR303 数据校验 , 这个就是我们可以在字段是增加一层过滤器验证 , 可以保证数据的合法性
复杂类型封装,yml 中可以封装对象 , 使用 value 就不支持
配置 yml 和配置 properties 都可以获取到值 , 强烈推荐 yml;
如果我们在某个业务中,只需要获取配置文件中的某个值,可以使用一下 @value
如果我们专门编写了一个 JavaBean 来和配置文件进行一一映射,就直接@configurationProperties
bean 映射 yaml 文件
松散绑定
Bean 的属性名和 yaml 中的表示方式支持使用:
- 驼峰式、下划线 (_)、短横线 (-) 后第一个表示大写字母
如 Bean 中属性的写法为
person.firstName- 方式一:
person.first-name - 方式二:
person.first_name
- 方式一:
如 Bean 中属性的写法为
person.first_name- 方式一:
person.first-name - 方式二:
person.firstName
- 方式一:
JSR303 数据校验
依赖
1
2
3
4<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
</dependency>Springboot 中可以用
@validated来校验数据,如果数据异常则会统一抛出异常,方便异常中心统一处理。我们这里来写个注解让我们的 name 只能支持 Email 格式;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9import javax.validation.constraints.Email;
//注册 bean
//数据校验
public class Person {
//name 必须是邮箱格式
private String email;
}配置文件
1
2person:
email: ABC123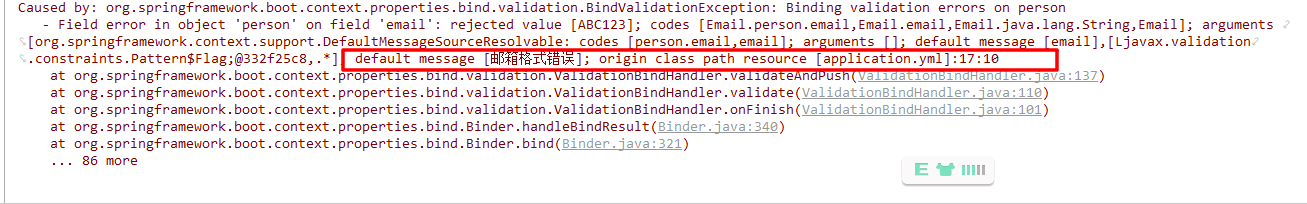
常见类型校验
常用如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
private String userName;
private int age;
private String email;
空检查
验证对象是否为 null
验证对象是否不为 null, 无法查检长度为 0 的字符串
检查约束字符串是不是 Null 还有被 Trim 的长度是否大于 0, 只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格。
检查约束元素是否为 NULL 或者是 EMPTY.(String ,Collection,Map 的 isEmpty() 方法)
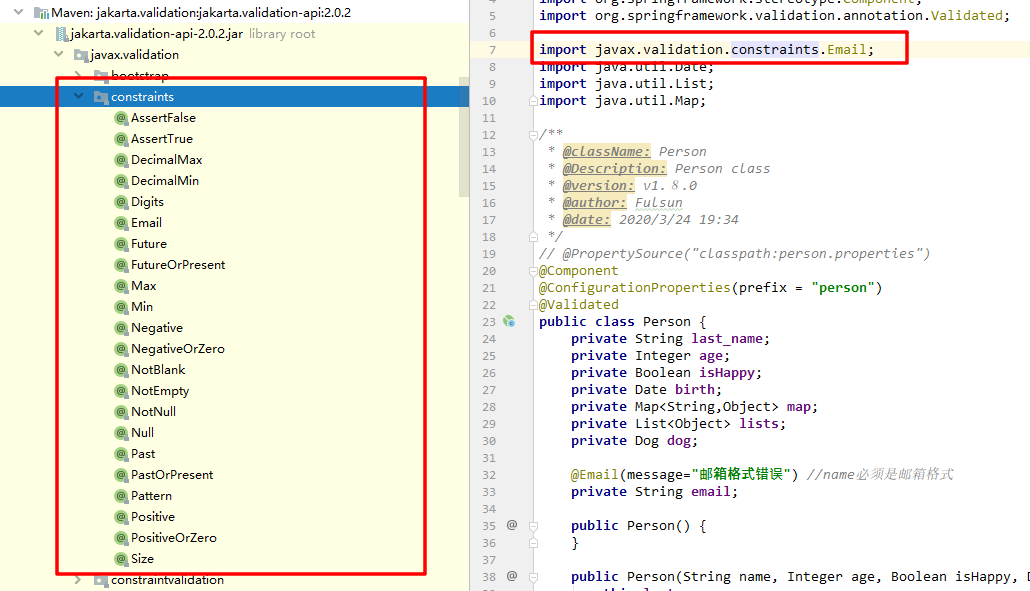
数值类型检查
检查约束元素的值必须大于等于指定的最小值jar 包下查看
Duration 类型
Spring Boot 内置支持从配置参数中解析 durations (持续时间),官网文档 给出了明确的说明
我们既可以配置毫秒数数值,也可配置带有单位的文本,配置 duration 不写单位,默认按照毫秒来指定,我们也可已通过 @DurationUnit 来指定单位:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
private Duration duration;
ns for nanoseconds (纳秒)
us for microseconds (微秒)
ms for milliseconds (毫秒)
s for seconds (秒)
m for minutes (分)
h for hours (时)
d for days (天)
DataSize 类型
与 Duration 的用法一模一样,默认单位是 byte (字节),可以通过 @DataSizeUnit 单位指定:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
private DataSize maxAttachmentSize = DataSize.ofMegabytes(2);
常见单位如下:
B for bytes
KB for kilobytes
MB for megabytes
GB for gigabytes
TB for terabytes
自定义类型
有些情况,我们想解析配置参数到我们自定义的对象类型上,假设,我们我们设置最大包裹重量:
1
private Weight maxAttachementWeight;
可以模仿 DataSize 和 Duration 创造自己的 converter (转换器)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
public class WeightConverter implements Converter<String,Weight> {
public Weight convert(String s) {
return null;
}
}将其注册到 Spring Boot 上下文中,
@ConfigurationPropertiesBinding注解是让 Spring Boot 知道使用该转换器做数据绑定1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class PropertiesConfig {
public WeightConverter weightConverter(){
return new WeightConverter();
}
}
多环境切换
- 实际开发中存在多种环境,profile 是 Spring 对不同环境提供不同配置功能的支持,可以通过激活不同的环境版本,实现快速切换环境;
多个配置文件写法
主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是
application-{profile}.properties/yml, 用来指定多个环境版本;YAML 配置文件示例
- dev 环境:
application-dev.properties - test 环境:
application-test.properties - prod 环境:
application-prod.properties
- dev 环境:
properties 配置文件示例
application-test.properties代表测试环境配置application-dev.properties代表开发环境配置
但是 Springboot 并不会直接启动这些配置文件,它
默认使用 application.properties 主配置文件;
单个配置文件写法
yml 支持使用三条短线
---可以作为分隔文档块,避免创建多个配置文件(不是很常用)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: demo #配置项目的访问路径
#选择要激活那个环境块
spring:
profiles:
active: prod #激活 prod 生产环境,因此端口为 8084
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev #配置环境的名称
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: prod #配置环境的名称
激活指定 profile
在 properties 配置文件中指定
1
spring.profiles.active=dev,db
在 YAML 配置文件中指定
1
2
3spring:
profiles:
active: prod命令行:在最后加上
--spring.profiles.active=dev1
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev;
虚拟机参数 vmoption:
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
配置文件的位置
- SpringBoot 加载配置文件的方式十分多,最常用的是在开发的资源文件中进行配置
项目加载顺序
springboot 启动会根据下面的优先级扫描位置下的
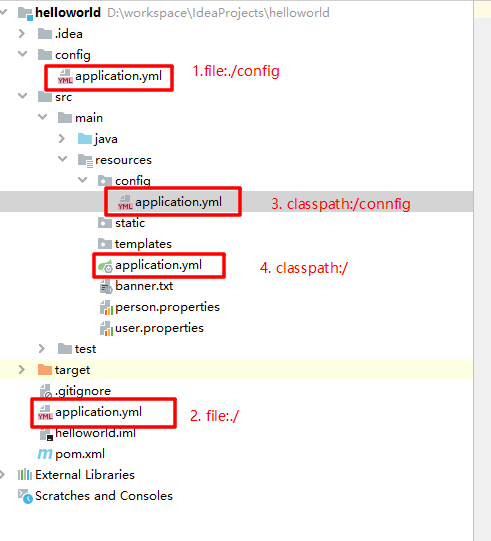
application.properties或application.yml文件作为默认配置文件,file 指的是项目根目录。优先级 位置 描述 优先级 1 file:./config/ 工程项目/config 高 2 file:./ 工程项目 较高 3 classpath:/config/ resources/config 较低 4 classpath:/ resources 低 优先级由高到低,先解析优先级低的配置文件,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置;
SpringBoot 会从这四个位置全部加载主配置文件,最后形成互补配置
外部配置加载顺序
SpringBoot 也可以从以下位置加载配置; 优先级从高到低;高优先级的配置覆盖低优先级的配置,所有的配置会形成互补配置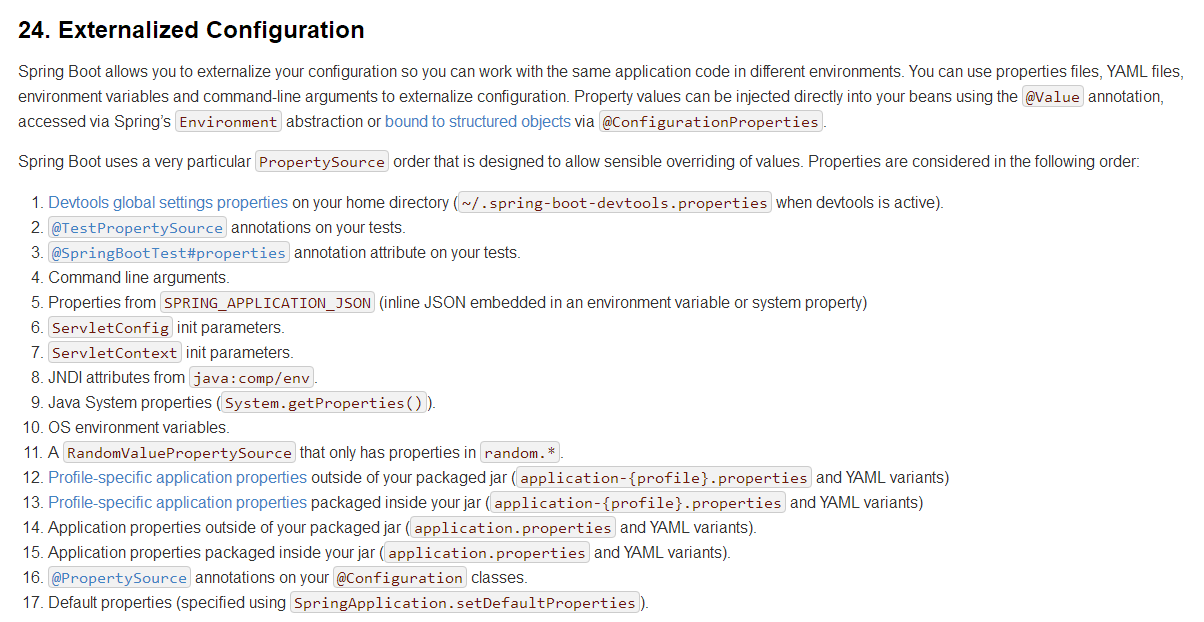
常用的 11 个位置 (优先级从高到低)
命令行参数:所有的配置都可以在命令行上进行指定,多个配置用空格分开;
--配置项=值1
2
3java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8087 --server.context-path=/abc
# 可以在代码中通过 setAddCommandLineProperties 来禁用
SpringApplication.setAddCommandLineProperties(false).来自 java:comp/env 的 JNDI 属性
Java 系统属性(System.getProperties())
操作系统环境变量
RandomValuePropertySource 配置的 random. *属性值
Jar 包寻找:顺序由 jar 包外向 jar 包内进行寻找,优先加载带 profile, 再来加载不带 profile
- jar 包外部的 application-{profile}.properties 或 application.yml(带 spring.profile) 配置文件
- jar 包内部的 application-{profile}.properties 或 application.yml(带 spring.profile) 配置文件
- jar 包外部的 application.properties 或 application.yml(不带 spring.profile) 配置文件
- jar 包内部的 application.properties 或 application.yml(不带 spring.profile) 配置文件
@Configuration 注解类上的@PropertySource
通过 SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties 指定的默认属性
运维小技巧
指定位置加载配置文件:通过
spring.config.location来改变默认的配置文件位置项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;这种情况,一般是后期运维做的多,相同配置,外部指定的配置文件优先级最高
1
java -jar spring-boot-config.jar --spring.config.location=F:/application.propert
bootstrap 与 application
加载顺序: 这里主要是说明 application 和 bootstrap 的加载顺序。
- bootstrap.yml(bootstrap.properties)先加载
- application.yml(application.properties)后加载
- bootstrap.yml 用于应用程序上下文的引导阶段。
- bootstrap.yml 由父 Spring ApplicationContext 加载。
- 父 ApplicationContext 被加载在 application.yml 的之前。
配置区别
bootstrap.yml 和 application.yml 都可以用来配置参数。
bootstrap.yml 可以理解成系统级别的一些参数配置,这些参数一般是不会变动的。
application.yml 可以用来定义应用级别的,如果搭配 spring-cloud-config 使用 application.yml 里面定义的文件可以实现动态替换。
使用 Spring Cloud Config Server 时,应在 bootstrap.yml 中指定:
1
2spring.application.name
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri
一些加密/解密信息
实例 bootstrap.yml :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14spring:
application:
name: service-a
cloud:
config:
uri: http://127.0.0.1:8888
fail-fast: true
username: user
password: ${CONFIG_SERVER_PASSWORD:password}
retry:
initial-interval: 2000
max-interval: 10000
multiplier: 2
max-attempts: 10当使用 Spring Cloud 时,通常从服务器加载“real”配置数据。为了获取 URL(和其他连接配置,如密码等),您需要一个较早的或“bootstrap”配置。因此,您将配置服务器属性放在 bootstrap.yml 中,该属性用于加载实际配置数据(通常覆盖 application.yml [如果存在] 中的内容)。
当然,在一些情况上不用那么区分这两个文件,你只需要使用 application 文件即可,把全部选项都写在这里,效果基本是一致的,在不考虑上面的加载顺序覆盖的问题上。
发布时间: 2020-03-22
最后更新: 2022-02-14
本文标题: SpringBoot 的配置文件
本文链接: https://fulsun.github.io/post/7c4c.html
版权声明: 本作品采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议进行许可。转载请注明出处!